Pagination & Search
Learn how to handle large datasets efficiently with pagination and search features.
What You'll Learn
- When to use pagination
- Creating paginated tables
- Adding search functionality
- Column-specific search
- Column selector feature
Why Pagination?
Displaying thousands of rows in a single table causes:
- Slow rendering - Windows struggles with 1000+ rows
- Poor UX - Users can't find data easily
- Memory issues - Large datasets consume resources
Solution: Pagination splits data into manageable pages.
Performance Benchmark
- Basic Table: Good for up to ~100 rows
- Paginated Table: Handles 100,000+ rows smoothly
Creating Paginated Tables
Basic Pagination
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/mansoldof/goTableView"
)
func main() {
// Create large dataset
data := [][]string{}
for i := 1; i <= 500; i++ {
data = append(data, []string{
fmt.Sprintf("%d", i),
fmt.Sprintf("Item %d", i),
fmt.Sprintf("$%.2f", float64(i)*10.5),
})
}
// Display with pagination (50 rows per page)
gotableview.NewPaginated("Large Dataset", 50).
Columns("ID", "Name", "Price").
Rows(data).
Show()
}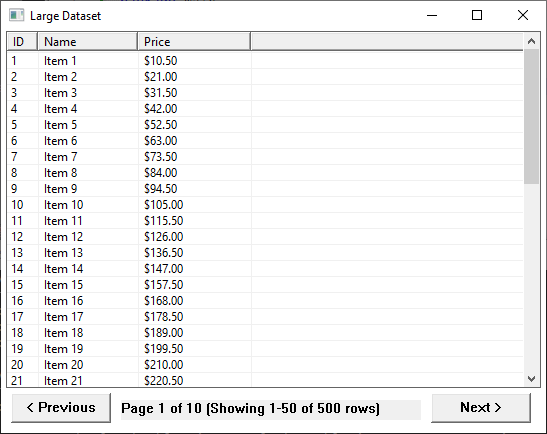
Key Points:
NewPaginated(title, pageSize)creates a paginated table- Page size determines rows per page
- Navigation buttons automatically added
- Page indicator shows current position
Page Size Guidelines
| Dataset Size | Recommended Page Size |
|---|---|
| 100-500 | 50 |
| 500-1,000 | 50-100 |
| 1,000-10,000 | 100 |
| 10,000+ | 100-200 |
// Small dataset
gotableview.NewPaginated("Small", 20).Columns(...).Rows(data).Show()
// Medium dataset
gotableview.NewPaginated("Medium", 50).Columns(...).Rows(data).Show()
// Large dataset
gotableview.NewPaginated("Large", 100).Columns(...).Rows(data).Show()Adding Search
Search All Columns
Add a search box that filters across all columns:
package main
import "github.com/mansoldof/goTableView"
func main() {
employees := [][]string{
{"Alice", "Engineering", "New York", "75000"},
{"Bob", "Sales", "Los Angeles", "60000"},
{"Carol", "Engineering", "Chicago", "70000"},
{"David", "Marketing", "New York", "65000"},
{"Eve", "Sales", "Miami", "62000"},
}
gotableview.NewPaginated("Employees", 50).
Columns("Name", "Department", "City", "Salary").
Rows(employees).
WithSearch(). // Enable search on all columns
Show()
}How It Works:
- Search box appears at the top
- Type to filter in real-time
- Search is case-insensitive
- Matches any column containing the text
- Pagination updates automatically
Column-Specific Search
Search only in specific columns by name:
gotableview.NewPaginated("Employees", 50).
Columns("Name", "Department", "City", "Salary").
Rows(employees).
SearchInColumns("Department", "City"). // Search only Department and City
Show()Benefits:
- Faster search (fewer columns to check)
- More precise results
- Clear indication of searchable columns
Search by Column Index
Use column indices instead of names:
gotableview.NewPaginated("Products", 50).
Columns("ID", "Name", "Category", "Price", "Stock").
Rows(products).
SearchInColumnIndices(1, 2). // Search columns 1 (Name) and 2 (Category)
Show()When to Use Indices
Use SearchInColumnIndices() when:
- Column names might change
- You're generating columns dynamically
- Working with unnamed columns
Column Selector
Let users choose which column to search:
package main
import "github.com/mansoldof/goTableView"
func main() {
products := [][]string{
{"001", "Laptop", "Electronics", "999.99", "15"},
{"002", "Desk", "Furniture", "299.99", "8"},
{"003", "Mouse", "Electronics", "24.99", "50"},
{"004", "Chair", "Furniture", "199.99", "12"},
}
gotableview.NewPaginated("Products", 50).
Columns("ID", "Name", "Category", "Price", "Stock").
Rows(products).
WithColumnSelector(). // Add dropdown for column selection
Show()
}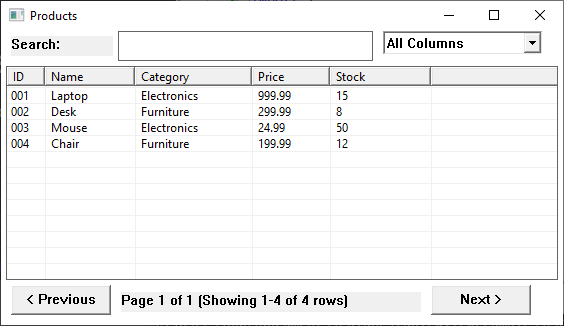
Features:
- Dropdown next to search box
- "All Columns" option (default)
- Each column listed individually
- Search updates when selection changes
Combining Features
Mix pagination, search, and column selection:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/mansoldof/goTableView"
)
type Transaction struct {
ID int `gotableview:"Transaction ID"`
Date time.Time `gotableview:"Date"`
Customer string `gotableview:"Customer"`
Product string `gotableview:"Product"`
Amount float64 `gotableview:"Amount"`
Status string `gotableview:"Status"`
}
func main() {
// Generate 1000 transactions
transactions := make([]Transaction, 1000)
for i := range transactions {
transactions[i] = Transaction{
ID: i + 1,
Date: time.Now().Add(-time.Duration(i) * time.Hour),
Customer: fmt.Sprintf("Customer %d", (i%50)+1),
Product: fmt.Sprintf("Product %s", string(rune('A'+(i%26)))),
Amount: float64(i%1000) + 0.99,
Status: []string{"Completed", "Pending", "Cancelled"}[i%3],
}
}
gotableview.FromStructsPaginated("Transactions", transactions, 100).
WithColumnSelector(). // User chooses search column
Show()
}Advanced Search Patterns
Search with Structs
type Employee struct {
ID int `gotableview:"Employee ID"`
Name string `gotableview:"Full Name"`
Department string `gotableview:"Department"`
Email string `gotableview:"Email"`
Phone string `gotableview:"Phone"`
}
employees := loadEmployees() // Load from database
gotableview.FromStructsPaginated("Employee Directory", employees, 50).
SearchInColumns("Full Name", "Department", "Email"). // Search specific fields
Show()Case-Sensitive Search (Future)
Currently, all searches are case-insensitive. This is intentional for better UX.
// Current behavior - case-insensitive
// Searching "engineering" matches "Engineering", "ENGINEERING", "engineering"
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("Name", "Department").
Rows(data).
WithSearch().
Show()Pagination Controls
The paginated table includes automatic controls:
Navigation Buttons
- < Previous: Go to previous page (disabled on first page)
- Next >: Go to next page (disabled on last page)
Page Indicator
Shows: Page X of Y (Showing A-B of C rows)
- X: Current page number
- Y: Total pages
- A-B: Row range on current page
- C: Total rows (filtered)
Search Box
- Real-time filtering
- Updates pagination automatically
- Shows filtered row count
Performance Tips
Optimize Page Size
// Too small - more page navigation needed
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 10).Rows(data).Show() // ❌
// Too large - slow rendering, defeats pagination purpose
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 1000).Rows(data).Show() // ❌
// Just right - balance between navigation and performance
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 100).Rows(data).Show() // ✅Search Performance
Column-specific search is faster:
// Slower - searches all 10 columns
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("Col1", "Col2", "Col3", "Col4", "Col5", "Col6", "Col7", "Col8", "Col9", "Col10").
Rows(data).
WithSearch().
Show()
// Faster - searches only 2 columns
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("Col1", "Col2", "Col3", "Col4", "Col5", "Col6", "Col7", "Col8", "Col9", "Col10").
Rows(data).
SearchInColumns("Col1", "Col2").
Show()Real-World Examples
Example 1: Log Viewer
package main
import (
"bufio"
"os"
"strings"
"github.com/mansoldof/goTableView"
)
func main() {
file, _ := os.Open("application.log")
defer file.Close()
var logs [][]string
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(file)
for scanner.Scan() {
line := scanner.Text()
parts := strings.SplitN(line, " ", 4)
if len(parts) >= 4 {
logs = append(logs, []string{
parts[0], // Timestamp
parts[1], // Level
parts[2], // Source
parts[3], // Message
})
}
}
gotableview.NewPaginated("Application Logs", 100).
Columns("Timestamp", "Level", "Source", "Message").
Rows(logs).
SearchInColumns("Level", "Message"). // Search by level or message
Show()
}Example 2: Database Explorer
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"github.com/mansoldof/goTableView"
)
type User struct {
ID int `gotableview:"ID"`
Username string `gotableview:"Username"`
Email string `gotableview:"Email"`
Status string `gotableview:"Status"`
CreatedAt string `gotableview:"Created"`
}
func main() {
db, _ := sql.Open("postgres", "connection_string")
defer db.Close()
rows, _ := db.Query("SELECT id, username, email, status, created_at FROM users ORDER BY id")
defer rows.Close()
var users []User
for rows.Next() {
var u User
rows.Scan(&u.ID, &u.Username, &u.Email, &u.Status, &u.CreatedAt)
users = append(users, u)
}
gotableview.FromStructsPaginated("User Database", users, 100).
WithColumnSelector(). // Let user choose search field
Show()
}Example 3: CSV Viewer
package main
import (
"encoding/csv"
"os"
"github.com/mansoldof/goTableView"
)
func main() {
file, _ := os.Open("large_dataset.csv")
defer file.Close()
reader := csv.NewReader(file)
records, _ := reader.ReadAll()
headers := records[0]
data := records[1:]
gotableview.NewPaginated("CSV Viewer", 100).
Columns(headers...).
Rows(data).
WithSearch(). // Search all columns
Show()
}Troubleshooting
Search Not Working
Make sure WithSearch() or SearchInColumns() is called:
// Wrong - no search ❌
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("A", "B").
Rows(data).
Show()
// Correct - search enabled ✅
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("A", "B").
Rows(data).
WithSearch().
Show()Column Names Not Found
Column names are case-sensitive:
// Wrong - case mismatch ❌
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("Name", "Department").
SearchInColumns("name", "department"). // Should be "Name", "Department"
Show()
// Correct ✅
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("Name", "Department").
SearchInColumns("Name", "Department").
Show()Page Count Wrong
Ensure data is added before Show():
// Wrong - data added after Show() ❌
table := gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).Columns("A", "B")
table.Show()
table.Rows(data) // Too late!
// Correct ✅
gotableview.NewPaginated("Data", 50).
Columns("A", "B").
Rows(data).
Show()What's Next?
- See Basic Examples for simple use cases
- Explore Advanced Examples
- Check the PaginatedTable API
Remember
For datasets over 100 rows, always use NewPaginated() instead of New() for better performance and user experience!
